*ADMISSIONS OPEN 2025-26* *LIMITED SEATS AVAILABLE*
Teaching Learning Methods
The Teaching-Learning Process (TLP) is designed to ensure students gain both theoretical knowledge and practical skills through structured and interactive learning methods.
Essential Aspects of the CSE Teaching-Learning Process
Subject Allocation & Planning: Subject allocation is determined based on the teaching statements submitted by faculty members and faculty prepare structured lesson plans, ensuring alignment with VTU syllabus and industry needs.
Teaching Methods: Use of ICT tools, flipped classrooms, peer learning, and interactive sessions for effective learning.
Course Evaluation: Internal assessments (IATs), quizzes, assignments, seminars, and mini-projects are part of the evaluation.
Course Outcomes & Skill Mapping: Subjects are mapped to Program Outcomes (POs) and Program Specific Outcomes (PSOs) to bridge curriculum gaps.
Learning Resources:
Concise Notes and Glossary of Terms for quick reference
Question Banks for self-assessment
Assignments & Tutorials to enhance problem-solving skills
Hands-on Learning:
- Lab Manuals & Practical Sessions for real-world problem-solving
- Projects & Faculty Showcases for application-based learning
- Flipped Classroom & Video Lectures to promote self-learning
Placements & Training: Industry-focused training in AI, ML, Big Data, Cloud Computing, and Android Development with top companies recruiting students.
This structured learning approach ensures students gain both theoretical knowledge and practical skills to excel in the industry.
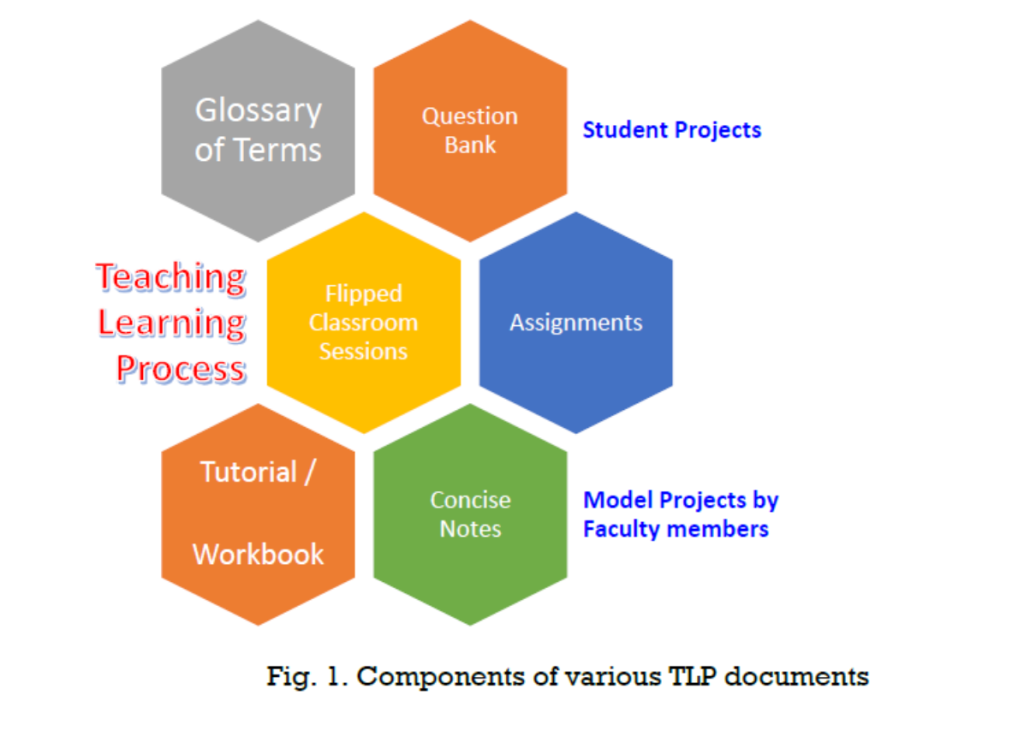
The image visually represents the Teaching-Learning Process (TLP) and its key components using a hexagonal layout. It highlights various essential documents that support effective learning:
- Glossary of Terms – Provides definitions and explanations of key concepts.
- Question Bank – A collection of important questions for self-assessment and exam preparation.
- Assignments – Tasks designed to reinforce learning and problem-solving skills.
- Tutorial/Workbook – Additional exercises to help students practice and understand concepts better.
- Flipped Classroom Sessions – Interactive learning approach where students engage with content before class.
- Concise Notes – Summarized study materials for quick revision.
Additionally, it mentions Student Projects and Model Projects by Faculty Members, emphasizing hands-on learning and practical exposure. The diagram effectively showcases how these components contribute to a structured and well-rounded Teaching-Learning Process.
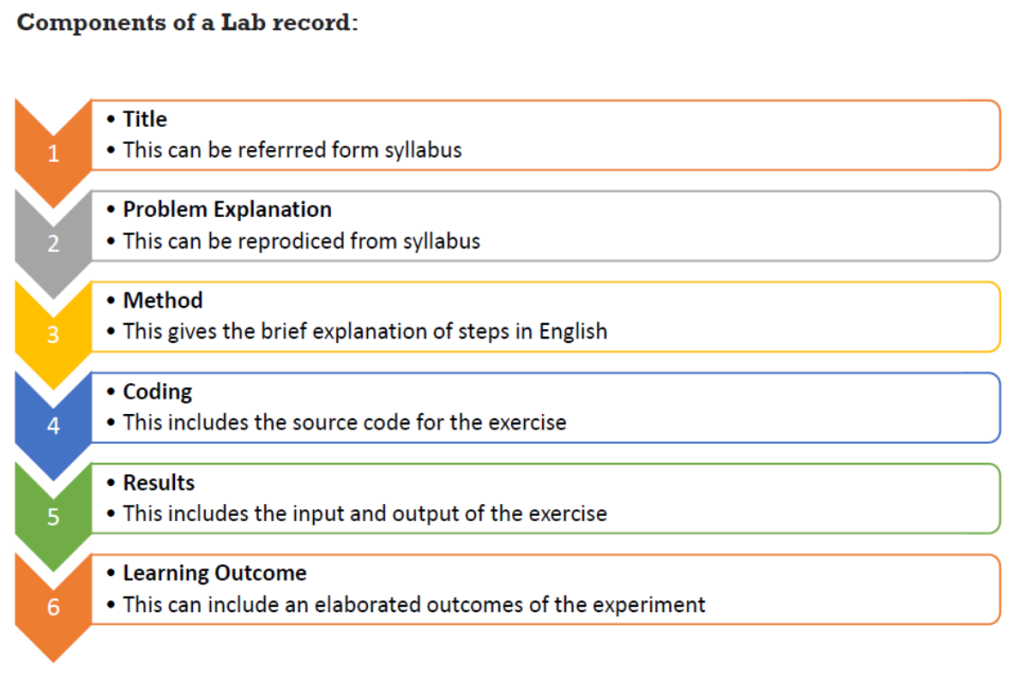
The image presents the Components of a Lab Record in a structured, step-by-step format using numbered sections with different colors. Here’s a breakdown of the components:
- Title – The name of the experiment, which can be referred to from the syllabus.
- Problem Explanation – A description of the problem statement, which can be reproduced from the syllabus.
- Method – A brief explanation of the steps involved in executing the experiment.
- Coding – The source code required for the exercise, applicable for programming-based labs.
- Results – Includes both input and output of the experiment, demonstrating its execution.
- Learning Outcome – A summary of the experiment’s key takeaways and conclusions.
This structured format ensures clarity, consistency, and ease of understanding for students while documenting their lab work.
Viva & Quiz in Labs: Students must answer viva questions during lab exercises to assess their understanding. A 10-mark quiz will be introduced in the final lab exam via a hard copy.
Faculty-Led Projects: Teachers develop and showcase sample applications related to the course, inspiring students to learn and engage actively.
Active Collaboration Hour (ACH)
Active Collaboration Hour (ACH) is a dedicated time for Course Instructors (CIs) teaching the same subject across different sections to come together. It serves as a platform for sharing best practices, addressing challenges, and exploring innovative teaching methodologies and technologies. Through collaborative discussions, faculty members can develop, refine, and enhance curriculum materials, ensuring a more effective and consistent learning experience for students.
Knowledge Reviewers
All course materials undergo review by the designated Knowledge Reviewers to ensure accuracy and quality.
This holistic approach of the Teaching- Learning process bridges the gap between academia and industry, fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, and lifelong learning, ultimately preparing students for successful careers in technology.